The Selection Inspector
Certain
attributes
of the current selection are shown
and can be changed in the Selection Inspector.
There are multiple ways to open this tool:
- with Actions... Inspect in the menu
- by clicking the button to the right of the
status line
- by choosing Inspect from the context menu obtained by
double-picking
an atom, bond, or pseudobond (that is, doubleclicking with the button
assigned to picking)
Items (levels) available for inspection:
Write List... brings up a dialog for
saving a parsable text file of specifications
for the selected items.
Write PDB... brings up a dialog for
saving the selection as a PDB file.
Close dismisses the Selection Inspector, while
Help opens this manual page in a browser window.
The descriptions in the Selection Inspector
are not necessarily the same as the attribute names.
If the selection includes multiple items of the same type
and their attribute values vary, "-- multiple --" or ">1"
will be reported for the attribute.
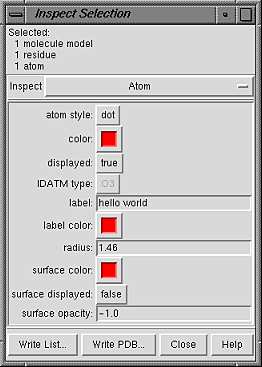 Atom attributes are:
Atom attributes are:
- atom style - atom draw mode
- color (a color well)
- color at the atom level;
see coloring hierarchy
- displayed - whether display is enabled at the atom level
(see display hierarchy)
- IDATM type - atom type
(currently shown in gray and cannot be changed)
- label - a text label for the atom.
If the atom label was shown using the menu or the
label command,
standard information (such as atom name) will be shown
in this field, but can be replaced arbitrarily;
however, showing the atom label again with the menu or
label
will restore the standard information.
- label color (a color well)
- if an atom label has no color of its own, it will inherit
the color of its associated atom; see
coloring hierarchy
- radius - radius in angstroms used when the
the draw mode is sphere; initially set
to an approximate VDW radius
- surface color (a color well)
- atom-level surface color; see
coloring hierarchy
- surface displayed - whether surface
display is enabled at the atom level
(see display hierarchy)
- surface opacity - atom-level surface opacity, ranging from
0 (completely transparent) to 1 (completely opaque); a negative value
indicates that the opacity included in the definition of the atom-level
surface color(s) should be used instead
Bond attributes are:
- bond style - bond draw mode
- color (a color well)
- color at the individual bond level (see
coloring hierarchy);
can also be controlled with the command
bondcolor.
Note that the color assigned to the bond will only be visible
when halfbond mode is off;
when halfbond mode is on, the color of each half of the bond
matches the visible color of the flanking atom.
- displayed - whether display is enabled at the individual
bond level (see display hierarchy);
can also be controlled with the command
bonddisplay
- true
- false
- if atoms shown
(displayed only when both flanking atoms are displayed)
- halfbond mode - whether the two halves of a bond are
handled as separate entities; when halfbond mode is on,
the color of each halfbond matches that of the attached atom
(can also be controlled with the command
bondcolor).
- label - an arbitrary text label for the bond
- label color (a color well)
- if a label has no color of its own, it will inherit
the color of its associated bond; see
coloring hierarchy
- radius - value to be multiplied by the molecule model
stick scale to generate
stick radius in angstroms (only applies to bonds in the stick
draw mode)
Residue attributes are:
- in helix
- in strand
- label - a text label for the residue.
If the residue label was shown using the menu or the
rlabel command,
standard information (such as residue name and number)
will be shown in this field, but can be replaced arbitrarily;
however, showing the residue label again with the menu or
rlabel
will restore the standard information.
- label color (a color well)
- if a residue label has no color of its own, it will inherit
the model color; see coloring hierarchy
- ribbon color (a color well)
- residue-level ribbon color;
see coloring hierarchy
- ribbon cross section - ribbon
style
(see also ribrepr)
- ribbon display
- whether ribbon is shown;
ribbons are only drawn for proteins and nucleic acids.
Protein secondary structure assignments are taken from the input structure
file or generated with ksdssp.
- ribbon scaling - ribbon
scaling
(see also ribscale)
Molecule model attributes are:
- active - whether the model is
activated for motion
- auto-chaining
- whether to connect atoms that precede and follow undisplayed segments
(whether to draw pseudobonds between them)
- ball scale
- scale factor for atoms in the ball
draw mode.
The ball scale is multiplied by individual atom
VDW radii to generate ball radii in angstroms.
- color (a color well)
- color at the model level;
see coloring hierarchy
- displayed - whether display is enabled at the model level
(see display hierarchy)
- line width - pixel width of lines depicting bonds
(when in the wire draw mode)
- ribbon hides backbone atoms - whether showing ribbon for
residues within the model hides backbone atoms for those residues
(see the command ribbackbone
for details)
- stick scale
- scale factor for bonds in the stick
draw mode.
The stick scale is multiplied by individual bond radii (default
0.2 angstroms) to generate stick radii in angstroms.
Changing stick scale is preferable to changing all of the bond radii
in a model, because the former will also scale singleton atoms in the
endcap draw mode appropriately. Either way,
the other endcap atoms (those participating in bonds) will be scaled
to match the thickest of the attached bonds.
- surface color (a color well)
- model-level surface color; see
coloring hierarchy
- surface opacity - model-level surface opacity,
ranging from 0 (completely transparent) to 1 (completely opaque);
a negative value indicates that the opacity included in the definition
of the model-level surface color should be used instead
- vdw density - relative density of dots used in any VDW surfaces
(as with the command vdwdensity)
- vdw dot size - pixel size of dots in any VDW surfaces
Pseudobond
attributes are:
- bond style - pseudobond draw mode
- color (a color well)
- color at the individual pseudobond level; see
coloring hierarchy.
Note that the color assigned to the pseudobond will only be visible
when halfbond mode is off;
when halfbond mode is on, the color of each half of the pseudobond
matches the visible color of the flanking atom.
- displayed - whether display is enabled at the individual
pseudobond level
(see display hierarchy)
- true
- false
- if atoms shown
(displayed only when both flanking atoms are displayed)
- halfbond mode - whether the two halves of a pseudobond are
handled as separate entities; when halfbond mode is on,
the color of each halfbond matches that of the attached atom.
- label - an arbitrary text label for the pseudobond.
If the pseudobond has already been given a label using
PseudoBond
Reader,
the label will be shown in this field, but can be replaced arbitrarily.
If the pseudobond is a distance monitor, however, this label reports the
measured distance and cannot be changed.
- label color (a color well)
- if a label has no color of its own, it will inherit
the color of its associated pseudobond; see
coloring hierarchy
- radius - value to be multiplied by the pseudobond group
stick scale to generate
stick radius in angstroms (only applies to pseudobonds in the stick
draw mode)
MSMS surface attributes are:
- active - whether the model is
activated for motion
- color source - whether the surface color reflects
the color at the model or atom level
(see coloring hierarchy). When surface
color is set independent of these levels, unknown is reported.
This occurs when the surface is custom-colored, for example with
Surface
Color.
- displayed - whether surface
display is enabled at the model level
(see display hierarchy)
- dot size - pixel size of dots used in the dot
surface representation
- line width - pixel width of lines used in the mesh
surface representation
- probe radius
- radius in Å of the probe sphere used to compute the surface.
A larger probe decreases surface bumpiness because it fits into fewer crevices.
A radius of 1.4 Å is commonly used to approximate a water molecule.
- representation - which type of
surface representation
is being used
- show disjoint surfaces - whether to check
for multiple disjoint surfaces rather than assuming there is only one
(increases calculation time)
- vertex density - vertices per Å2
used to compute the surface.
Greater density results in a smoother surface but
increases computational demands for calculating and moving the surface.
UCSF Computer Graphics Laboratory / August 2007
 Atom attributes are:
Atom attributes are: